You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Despite Overwhelming Evidence, Creationists Cling to Unreality
- Thread starter DeathEatsaCracker
- Start date
<!-- / close content container --><!-- open content container -->Great idea!
IMO, Parent would do a better job than many of the tenured teachers union hacks who toe the party line while failing to be teachers,
Look at the drop out rate in the inner cities - 50% plus - the teachers unions have failed those who need an education the most.
<TABLE class=tborder style="BORDER-TOP-WIDTH: 0px" cellSpacing=1 cellPadding=6 width="100%" align=center border=0><TBODY><TR><TD class=thead colSpan=2>08-10-2008 01:03 PM</TD></TR><TR title="Post 5635881" vAlign=top><TD class=alt1 align=middle width=125>punter</TD><TD class=alt2>LET PARENTS DECIDE!
Might as well let them grade the math and spelling also. </TD></TR></TBODY></TABLE>
Might as well let them grade the math and spelling also. </TD></TR></TBODY></TABLE>
IMO, Parent would do a better job than many of the tenured teachers union hacks who toe the party line while failing to be teachers,
Look at the drop out rate in the inner cities - 50% plus - the teachers unions have failed those who need an education the most.
BTW - It's the anti-christian bigots who want their theory of evolution taught to the exclusion of all else.
Their bigoted hatred of religion and the solace that believers find in God is reminiscent of the KKK who hated everyone who was different.
I can't find it in me to hate such bigoted minds - God has taught me that hate and bigotry are wrong -but I do pity them for not having the peace and comfort that God brings to a soul - because of Gods gift, I'm not afraid to admit when I'm wrong - and I'm not afraid to fight when I'm right.
Their bigoted hatred of religion and the solace that believers find in God is reminiscent of the KKK who hated everyone who was different.
I can't find it in me to hate such bigoted minds - God has taught me that hate and bigotry are wrong -but I do pity them for not having the peace and comfort that God brings to a soul - because of Gods gift, I'm not afraid to admit when I'm wrong - and I'm not afraid to fight when I'm right.
BTW - It's the anti-christian bigots who want their theory of evolution taught to the exclusion of all else.
Their bigoted hatred of religion and the solace that believers find in God is reminiscent of the KKK who hated everyone who was different.
I can't find it in me to hate such bigoted minds - God has taught me that hate and bigotry are wrong -but I do pity them for not having the peace and comfort that God brings to a soul - because of Gods gift, I'm not afraid to admit when I'm wrong - and I'm not afraid to fight when I'm right.
BB why would we have schools teach a religious belief? You ever hear about seperation of church and state?
I learned about religious things in my house and church. It is up to the parents to teach these things. You call yourself conservative but when it comes to religion you want the state teaching our kids religious beliefs....how is that conservative?
Hey when have you admitted you are wrong on ths forum? Just curious.
BTW - It's the anti-christian bigots who want their theory of evolution taught to the exclusion of all else.
Their bigoted hatred of religion and the solace that believers find in God is reminiscent of the KKK who hated everyone who was different.
I can't find it in me to hate such bigoted minds - God has taught me that hate and bigotry are wrong -but I do pity them for not having the peace and comfort that God brings to a soul - because of Gods gift, I'm not afraid to admit when I'm wrong - and I'm not afraid to fight when I'm right.
BB why would we have schools teach a religious belief? You ever hear about seperation of church and state?
I learned about religious things in my house and church. It is up to the parents to teach these things. You call yourself conservative but when it comes to religion you want the state teaching our kids religious beliefs....how is that conservative?
Hey when have you admitted you are wrong on ths forum? Just curious.
One theory is based on millions of fossils and a myriad of scientific methods the other is based on faith in early chapters of one book. That book has been interpreted many times.
the 6000 year old earth was a result of king James' clerics calculations. I'm sure they had better scientific methods 600 years ago. Sheesh.
the 6000 year old earth was a result of king James' clerics calculations. I'm sure they had better scientific methods 600 years ago. Sheesh.
BB why would we have schools teach a religious belief? You ever hear about seperation of church and state?
I learned about religious things in my house and church. It is up to the parents to teach these things. You call yourself conservative but when it comes to religion you want the state teaching our kids religious beliefs....how is that conservative?
Hey when have you admitted you are wrong on ths forum? Just curious.
why would we have schools teach a religious belief?
Are you trying to tello me that Darwins THEORY of Eveolution is not a religious belief?
One theory is based on millions of fossils and a myriad of scientific methods the other is based on faith in early chapters of one book. That book has been interpreted many times.
the 6000 year old earth was a result of king James' clerics calculations. I'm sure they had better scientific methods 600 years ago. Sheesh.
What about ID?
Why do the Darwinists continue to exclude ID as a plausible "theory"?
Those who are in strong support of Darwinism tend to get their relgious doctrine from the Manifesto (whether they know it or not) and consider anything that supports their religion to be factual while doing everything in their power to undermine those "isms" they disagree with.
What about ID?
Why do the Darwinists continue to exclude ID as a plausible "theory"?
Those who are in strong support of Darwinism tend to get their relgious doctrine from the Manifesto (whether they know it or not) and consider anything that supports their religion to be factual while doing everything in their power to undermine those "isms" they disagree with.
Isnt it the same for both sides?
Guess I deserve it. My daddy told me "never argue with a fool. A passerby might not know the difference".
Thanks for proving my point.
You go out of your way to diminish my belief without proving that yours is the exacting truth and you call me a fool.
I agree that the 5,000 or 6,000 year time frame is an extreme that some very ardent Christians adhere to - but I would never try to belittle their belief because I don't necessarily agree with them.
I also agree that the Darwinists are just as extreme as those Christians in demanding that their belief is the only true belief. And I haven't tried to diminish Darwinism - it has a lot of merits.
Normally, I let sleeping dogs lay, but the Darwinists have demanded that all other beliefs be excluded from the lexicon.
So why am I a fool for such thinking?
I really dont give a shit what people believe but when they want to start teaching creationism in school, that is teaching religion because other than faith there is nothing to suggest that a literal translation of biblical creation is anything else.
Also to say that the theory of evolution not be taught is also interference by religion in public school.
Agree 100 % [You're still a prick though] :lol:
The OldTestament believers shouldn't be wasting valuable time lecturing apathetic sports handicappers. They would be better served instead alerting the biology and anthropology departments at the thousands of universities and advanced education institutions across the USA that teach the lessons learned by Darwin and other scientists over the past couple centuries.
Let these poor misguided professors and academics know that the Earth is only 6500 years old and get them into line!
Let these poor misguided professors and academics know that the Earth is only 6500 years old and get them into line!
The OldTestament believers shouldn't be wasting valuable time lecturing apathetic sports handicappers. They would be better served instead alerting the biology and anthropology departments at the thousands of universities and advanced education institutions across the USA that teach the lessons learned by Darwin and other scientists over the past couple centuries.
Let these poor misguided professors and academics know that the Earth is only 6500 years old and get them into line!
Barman,
Are these the misguided professors and academics that have
continually pushed fraudulent evidence to support their false
religion of Darwinism?
November 21, 2002 Scientific American Magazine
Second Piece of Fossil Forgery Identified
By Sarah Graham
<!--/end related-->
<!--/end headline-->
<!-- featured article END -->






<script type="text/javascript" language="JavaScript">digg_url = newURL;digg_skin = 'compact';digg_window = 'new';digg_title = newTitle;digg_bgcolor = 'none';</script> <script src="http://www.sciam.com/assets/js/diggthis.js" type="text/javascript"></script><iframe src="http://digg.com/tools/diggthis.php?u=http%3A//www.sciam.com/article.cfm%3Fid%3Dsecond-piece-of-fossil-fo&t=Second%20Piece%20of%20Fossil%20Forgery%20Identified%3A%20Scientific%20American&w=new&k=none&s=compact" name="diggiframe" scrolling="no" width="106" frameborder="0" height="18"></iframe>

 <script>facebook_url = "http://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=" + encodeURIComponent(newURL) + "&t=" + encodeURIComponent(newTitle);</script> <script>function fbs_click() {u=location.href;t=document.title;window.open(facebook_url,'sharer','toolbar=0,status=0,width=626,height=436');return false;}</script>
<script>facebook_url = "http://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=" + encodeURIComponent(newURL) + "&t=" + encodeURIComponent(newTitle);</script> <script>function fbs_click() {u=location.href;t=document.title;window.open(facebook_url,'sharer','toolbar=0,status=0,width=626,height=436');return false;}</script>

 <script>reddit_url = newURL;reddit_title = newTitle</script> <script type="text/javascript" src="http://reddit.com/button.js?t=1&width=120&height=20"></script><iframe src="http://www.reddit.com/button_content?t=1&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.sciam.com%2Farticle.cfm%3Fid%3Dsecond-piece-of-fossil-fo&title=Second%20Piece%20of%20Fossil%20Forgery%20Identified%3A%20Scientific%20American" scrolling="no" width="120" frameborder="0" height="20"></iframe>
<script>reddit_url = newURL;reddit_title = newTitle</script> <script type="text/javascript" src="http://reddit.com/button.js?t=1&width=120&height=20"></script><iframe src="http://www.reddit.com/button_content?t=1&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.sciam.com%2Farticle.cfm%3Fid%3Dsecond-piece-of-fossil-fo&title=Second%20Piece%20of%20Fossil%20Forgery%20Identified%3A%20Scientific%20American" scrolling="no" width="120" frameborder="0" height="20"></iframe> <!-- article START -->

INSTITUTE OF VERTEBRATE PALEONTOLOGY AND PALEOANTHROPOLOGY
<script type="text/javascript"> aArticleImages = new Array; aArticleImages[0] = new Object; aArticleImages[0].title = ""; aArticleImages[0].caption = ""; aArticleImages[0].credit = "INSTITUTE OF VERTEBRATE PALEONTOLOGY AND PALEOANTHROPOLOGY"; aArticleImages[0].url = ""; aArticleImages[0].alt = "Archaeoraptor fossil"; aArticleImages[0].src = "/media/inline/000D8732-EA5D-1DDB-A838809EC588F2D7_1.jpg"; aArticleImages[0].thisImageNumber = "1"; </script>
Discovered in 1999, the fossil Archaeoraptor was briefly believed to be the missing link between dinosaurs and birds. Shortly after its unveiling, however, it was determined that Archaeoraptor was instead a fake, probably comprised of up to five specimens of two or more different species. In 2000, scientists identified its tail as that of a Microraptor dinosaur from the early Cretaceous period. Now a report published today in the journal Nature classifies the rest of the faked fossil as the remains of a fish-eating bird.
Zhonghe Zhou and Fucheng Zhang of the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology in Beijing and Julia A. Clarke of the American Museum of Natural History in New York City made the assessment by comparing Archaeoraptor to the fossil bird Yanornis martini. Both the dimensions and anatomical features of the front half of the fossil forgery, including the legs, toes, and beak tip, correspond very closely to those of Y. martini, the team reports. In fact, once breakage is taken into consideration, they are nearly identical. The researchers also analyzed a third, previously undescribed specimen that was recently retrieved from the same fossil-rich region of China and determined that it was also a Yanornis. Digested fish remains preserved in the creature's gut provided scientists with a peek into Y. martini's dietary preferences.
National Geographic printed articles about the hoax after being
warned that it was a forgery by over-zealous Darwinists.
National Museum of Natural History
Smithsonian Institution
Washington, D. C. 20560
1 November 1999
OPEN LETTER TO:
Dr. Peter Raven, Secretary
PRaven@nas.org
Committee for Research and Exploration
National Geographic Society
Washington, DC 20036
Dear Peter,
I thought that I should address to you the concerns expressed below because your committee is at least partly involved and because you are certainly now the most prominent scientist at the National Geographic Society.
With the publication of “Feathers for T. rex?” by Christopher P. Sloan in its November issue, National Geographic has reached an all-time low for engaging in sensationalistic, unsubstantiated, tabloid journalism. But at the same time the magazine may now claim to have taken its place in formal taxonomic literature.
Although it is possible that Mr. Czerkas “will later name” the specimen identified on page 100 as Archaeoraptor liaoningensis, there is no longer any need for him to do so.
Because this Latinized binomial has apparently not been published previously and has now appeared with a full-spread photograph of the specimen “accompanied by a description or definition that states in words characters that are purported to differentiate the taxon,” the name Archaeoraptor liaoningensis Sloan is now available for purposes of zoological nomenclature as of its appearance in National Geographic (International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, Article 13a, i). This is the worst nightmare of many zoologists—that their chance to name a new organism will be inadvertently scooped by some witless journalist. Clearly, National Geographic is not receiving competent consultation in certain scientific matters.
Sloan’s article explicitly states that the specimen in question is known to have been illegally exported and that “the Czerkases now plan to return it to China.” In Washington, in June of 1996, more than forty participants at the 4th International Meeting of the Society of Avian Paleontology and Evolution, held at the Smithsonian Institution, were signatories to a letter to the Director of the Chinese Academy of Sciences that deplored the illegal trade in fossils from China and encouraged the Chinese government to take further action to curb this exploitation.
There were a few fossil dealers at that meeting and they certainly got the message. Thus, at least since mid-1996 it can hardly have been a secret to anyone in the scientific community or the commercial fossil business that fossils from Liaoning offered for sale outside of China are contraband.
Most, if not all, major natural history museums in the United States have policies in effect that prohibit their staff from accepting any specimens that were not legally collected and exported from the country of origin. The National Geographic Society has not only supported research on such material, but has sensationalized, and is now exhibiting, an admittedly illicit specimen that would have been morally, administratively, and perhaps legally, off-limits to researchers in reputable scientific institutions.
Prior to the publication of the article “Dinosaurs Take Wing” in the July 1998 National Geographic, Lou Mazzatenta, the photographer for Sloan’s article, invited me to the National Geographic Society to review his photographs of Chinese fossils and to comment on the slant being given to the story. At that time, I tried to interject the fact that strongly supported alternative viewpoints existed to what National Geographic intended to present, but it eventually became clear to me that National Geographic was not interested in anything other than the prevailing dogma that birds evolved from dinosaurs.
Sloan’s article takes the prejudice to an entirely new level and consists in large part of unverifiable or undocumented information that “makes” the news rather than reporting it. His bald statement that “we can now say that birds are theropods just as confidently as we say that humans are mammals” is not even suggested as reflecting the views of a particular scientist or group of scientists, so that it figures as little more than editorial propagandizing. This melodramatic assertion had already been disproven by recent studies of embryology and comparative morphology, which, of course, are never mentioned.
More importantly, however, none of the structures illustrated in Sloan’s article that are claimed to be feathers have actually been proven to be feathers. Saying that they are is little more than wishful thinking that has been presented as fact. The statement on page 103 that “hollow, hairlike structures characterize protofeathers” is nonsense considering that protofeathers exist only as a theoretical construct, so that the internal structure of one is even more hypothetical.
The hype about feathered dinosaurs in the exhibit currently on display at the National Geographic Society is even worse, and makes the spurious claim that there is strong evidence that a wide variety of carnivorous dinosaurs had feathers. A model of the undisputed dinosaur Deinonychus and illustrations of baby tyrannosaurs are shown clad in feathers, all of which is simply imaginary and has no place outside of science fiction.
The idea of feathered dinosaurs and the theropod origin of birds is being actively promulgated by a cadre of zealous scientists acting in concert with certain editors at Nature and National Geographic who themselves have become outspoken and highly biased proselytizers of the faith. Truth and careful scientific weighing of evidence have been among the first casualties in their program, which is now fast becoming one of the grander scientific hoaxes of our age—the paleontological equivalent of cold fusion. If Sloan’s article is not the crescendo of this fantasia, it is difficult to imagine to what heights it can next be taken. But it is certain that when the folly has run its course and has been fully exposed, National Geographic will unfortunately play a prominent but unenviable role in the book that summarizes the whole sorry episode.
Sincerely,
Storrs L. Olson
Curator of Birds
National Museum of Natural History
Smithsonian Institution
Washington, DC 20560
Darwinists have been pushing fraudulent evidence from the
beginning of their false religion.
Piltdown man: Found in a gravel pit in Sussex England in 1912, this fossil was considered by some sources to be the second most important fossil proving the evolution of man—until it was found to be a complete forgery 41 years later. The skull was found to be of modern age. The fragments had been chemically stained to give the appearance of age, and the teeth had been filed down!
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Piltdown_Man
I'll let the reader do the research into the many other ape forgeries
touted by the Darwinian lemmings, including Nebraska Man, Java man,
Neanderthal Man, Orce Man...
beginning of their false religion.
Piltdown man: Found in a gravel pit in Sussex England in 1912, this fossil was considered by some sources to be the second most important fossil proving the evolution of man—until it was found to be a complete forgery 41 years later. The skull was found to be of modern age. The fragments had been chemically stained to give the appearance of age, and the teeth had been filed down!
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Piltdown_Man
I'll let the reader do the research into the many other ape forgeries
touted by the Darwinian lemmings, including Nebraska Man, Java man,
Neanderthal Man, Orce Man...
I have to include one more notable ape fraud touted by
the religion of Darwinism:
<center>UN-ETHICAL EXAMPLES OF ACADEMIC LICENSE OR FRAUD BY SELF AGGRANDIZING (MACRO-EVOLUTIONARY) "EXPERTS" WHO HOLD THEIR INTERPRETATIONS TO BE INFALLIBLY TRUE.</center>
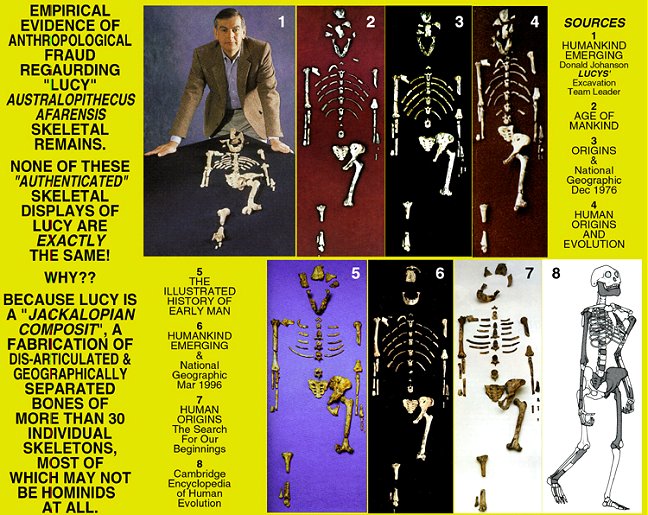
<center>COMMON SENSE & REASON, NOT TO MENTION EMPIRICALLY CONSISTENT EVIDENCE, "REQUIRE" THE EXACT SAME BONES BE PHOTOGRAPHICALLY REPRESENTED EVERY TIME THEY'RE SHOWN! ARBITRARILY ASSEMBLING BONES FROM A PILE IN YOUR LAB AND THEN PRESENTING THEM AS "PROOF" OF YOUR ORIGINAL FIND IS THE HEIGHT OF ACADEMIC ARROGANCE, UN-PROFESSIONAL SCIENCE AND EMPIRICAL FRAUD. METAPHYSICAL SCIENCE IS A "RELIGION" THAT ARBITRARILY DEFINES WHAT IS TRUE AND REJECTS ANY EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE THAT FALSIFIES IT!</center>
the religion of Darwinism:
<center>UN-ETHICAL EXAMPLES OF ACADEMIC LICENSE OR FRAUD BY SELF AGGRANDIZING (MACRO-EVOLUTIONARY) "EXPERTS" WHO HOLD THEIR INTERPRETATIONS TO BE INFALLIBLY TRUE.</center>

<center>COMMON SENSE & REASON, NOT TO MENTION EMPIRICALLY CONSISTENT EVIDENCE, "REQUIRE" THE EXACT SAME BONES BE PHOTOGRAPHICALLY REPRESENTED EVERY TIME THEY'RE SHOWN! ARBITRARILY ASSEMBLING BONES FROM A PILE IN YOUR LAB AND THEN PRESENTING THEM AS "PROOF" OF YOUR ORIGINAL FIND IS THE HEIGHT OF ACADEMIC ARROGANCE, UN-PROFESSIONAL SCIENCE AND EMPIRICAL FRAUD. METAPHYSICAL SCIENCE IS A "RELIGION" THAT ARBITRARILY DEFINES WHAT IS TRUE AND REJECTS ANY EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE THAT FALSIFIES IT!</center>